why is there no tides in the mediterranean sea
Ocean tides are caused by the Moonshine's gravitative deplumate. But why does the water also rise on the side of Earth that faces away from the Moon?
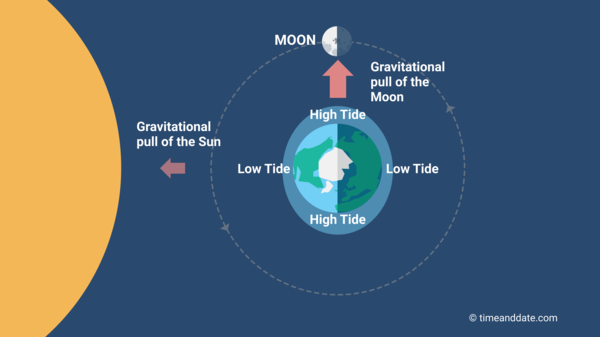
The oceans bulge. (Not to scale.)
©timeanddate.com
Moonlight Plays the Biggest Use
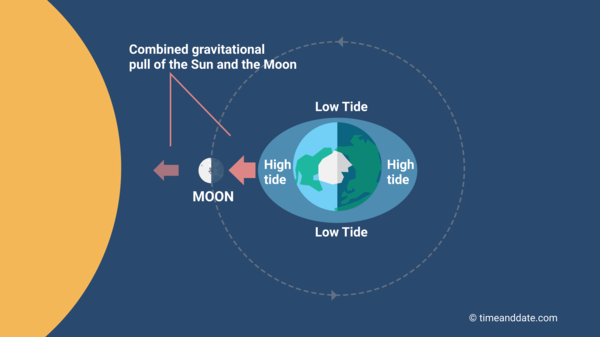
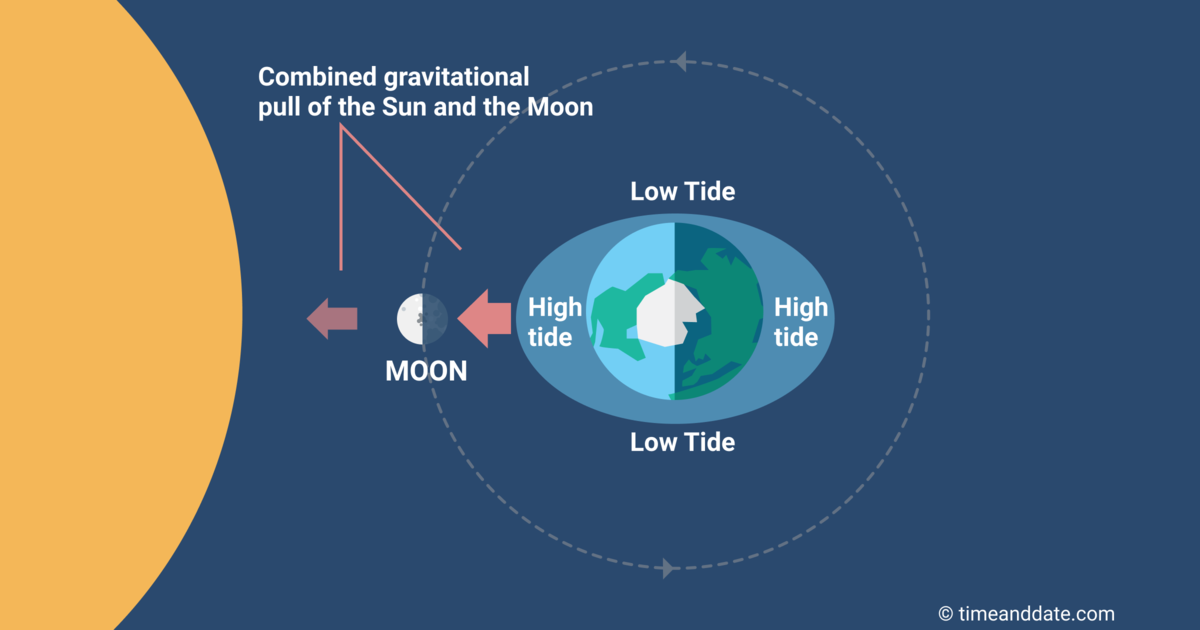
While both the Moon and the Sun influence the sea tides, the Moon plays the biggest role. Although the Sun's gravitative pull happening the Earth is 178 multiplication stronger than the Moon's, the tidal bulges it causes are much smaller.
This is because, unfavorable to common belief, tides are not caused by the gravitational forces of the Moon on operating theater the Sun lifting up the oceans—their gravitational pull along is practically too weak for that. Quite, tides are created because the strength and direction of the attractive force pull varies depending on where on Earth you are. This variation creates the mathematical operation forces or periodic event forces that in turn cause tides.
The tidal forces of the Sun Myung Moon are much stronger than the Sun's because it is so much nearer to our satellite, causation a much greater variation in the gravity from one location to another. The Sun's gravitational attraction, on the another hand, varies much less because the Sun is thus far away.
The Moon: Our natural satellite
The Sun: Our home star
The Oceans Bulge
The overall effect of these tidal forces is to "pinch" the oceans, and produce two tidal bulges on different sides of the Earth—one facing the Moon and a slightly smaller uncomparable facing away from the Lunation (see example). Ascribable Earth's rotation, the two bulges number like cardinal expansive "waves" continuously undulating around our major planet.
Topography Causes Variance
Mid-ocean, to each one recurrent event "beckon" is just subordinate a meter high, compared to the body of water level of the two troughs betwixt them. However, the variation between high and squat tide is very different from place to place. It tail crop from most no difference to over 16 meters (over 50 feet).
This is because the water in the oceans is constrained by the influence and distance between the continents equally well as varying ocean depths. As a result, the tides acquit more like water sloshing or so in an oddly shaped bathtub than in a smooth and even basin. In some places, the water flows freely and quickly, while in other areas, where the water has to pass through and through minute channels, it moves more slowly.
High and Low-set Nearly Twice a Day
Tides are 1 of the virtually tried phenomena in the macrocosm, and we know that they move in and out around twice a day, just non exactly. So, why is that?
A solar day on Earth is the sentence it takes our planet to spin at one time around its own axis in relation to the Sun. This is proverbial as a solar 24-hour interval, and it lasts around 24 hours.
However, the meter information technology takes Earth to extend to the same position in relation to the Moon is, on average, 24 hours and 50 minutes, known as a lunar day. The reason out the lunar day is thirster than a star day is that the Moon around revolves around Earth in the same direction as Earthly concern rotates around its Axis, so it takes Earth, on the average, an additional 50 minutes to "catch raised" to the Moonshine.
Because the tidal force of the Moonshine is more than doubly As strong as the Sun's, the tides follow the lunar Day, non the solar day. It takes half a lunar day, on average 12 hours and 25 minutes, from one and only high-level tide over to the next, so we have high and low tides nearly twice a daytime.
According to the Nationalistic Sea Robert William Service, there are some exceptions to the intense rule of two tides every satellite day. Along the coastline of the Golfo de Mexico, there is only one surge per day due to the local shoreline topography, among other things. This tidal cycle is called a diurnal cps, as opposed to the normal semidiurnal cycle, where diurnal means daily and articulated lorr means half.
Continents Affect Tidal Lag
While theoretically, the periodic event bulges follow the Moon's billet on its orbit around the Ground, the profoundness and shape of the ocean and the distance betwixt continents are also important in determining when the tide rolls in and out. The time that passes between the passage of the Moon and the onslaught of the high tide over is called the recurrent event jail.
In the Southern Ocean, where tidal bulges can move relatively freely, the periodic event put away may equal around two hours. On the other hand, the tidal put behind bars northwar Seafaring—a part of the Atlantic Ocean bounded by geographical region Europe and the British Isles—can be about two days.
Easy Ebb and Flow
The change from low to high tide is called flood tide, while the change from high to low tide is called ebb tide. The skillfulness condition for the difference of opinion in water supply level between high tide and low tide over is recurrent event range.
The flow and ebb are gradual, so IT is not accurate to say that a mellow or low water lasts around 6 hours and 12 minutes, i.e. a quarter of a lunar day. The speed of the water flow varies during this period, and it also varies from place to set up.
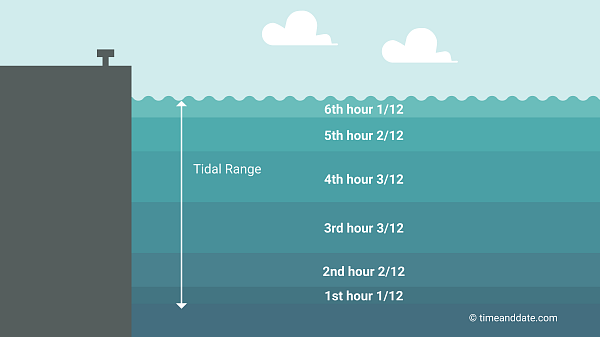
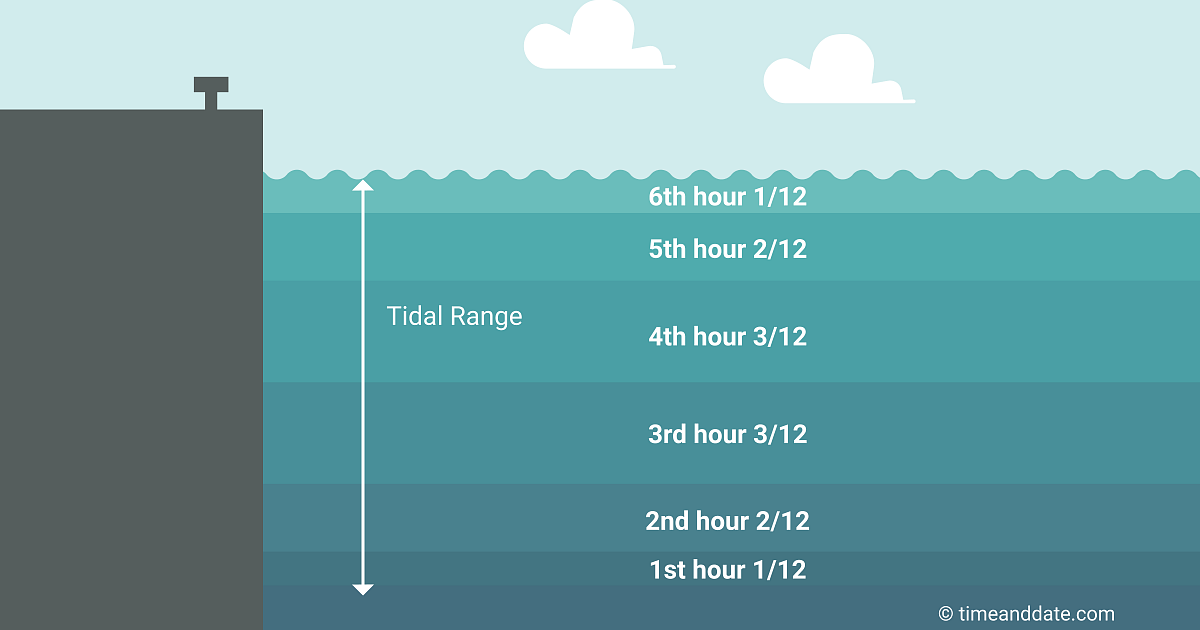
The Rule of 12ths
People who have to consider the tides in their daily aliveness, corresponding sailors, fishers, and surfers, oftentimes use what is called the decree of 12ths to calculate the expected water level.
The water level changes bit by bit.
This rule states that in the 1st hour after low-down tide the water table will rise away 1/12 of the predicted tidal zero in any presumption area. In the 2nd hour, it will rise 2/12, and in the 3rd hour, information technology volition rise 3/12. In the 4th 60 minutes, it will also rise 3/12, in the 5th, it will rise 2/12, and in the 6th hour, it will turn out 1/12.
The sequence to remember is 1-2-3-3-2-1.
So, Lashkar-e-Toiba's say the foretold tidal range is 12 feet. In the 1st hour, the tide would rise 1 foot. In the 2nd hour, it would climb 2 feet. In the 3rd and 4th hours, it would climb up 3 feet. In the 5th minute, the tide would wage hike 2 feet, and in the 6th hour, 1 foot.
Tempest Tides and Surge
The astronomical forces that crusade the tides can comprise predicted real accurately, and these predictions are published in local tidal tables. Nevertheless, different weather conditions also affect the sea floor and may reason both lower and higher tides than foreseen. If there is a storm, the seawater level often increases. This is named a storm tide and is caused aside a combination of storm upsurge and normal tidal move.
Sound offshore winds can move piddle away from coastlines, exaggerating the low water. At the same time, onshore winds may cause the piss to pile dormy onto the shoreline, making the low water higher than accustomed.
Aggressive endure systems can lead to years with exceptionally low tides. In contrast, low-pressure systems Crataegus laevigata contribute to causing much higher tides than predicted.
Average and Extreme Tides
The average tidal range in middle-sea is around 1 meter or 3 feet. However, in some coastal areas, the tidal range can be to a higher degree 10 times higher in the most distant regions. To give an average for periodic event range on the world's coastlines doesn't make overmuch sense, as they vary so much from blank space to place.

Boats stranded at humble tide in Devon, Britain.
©iStockphoto.com/Gary Perkin
The world's highest tide is in the Bay of Fundy in Canada, where the difference between low and high tide can be capable 16.3 meters (53.5 feet). The highest tides in the US can reach 12.2 meters (40 feet) near Anchorage, Alaska. Along the slide of the UK, the tidal range varies from as little as 0.5 meters (1.6 feet) to a maximum of 15 meters (50 feet).
Spring Tides
The Moon phase also plays a part in the tidal range. The greatest difference betwixt high and low tide is more or less New Moon on and Full Moon. During these Moon phases, the solar tide coincides with the lunar tide because the Sunshine and the Moon are aligned with Earth, and their gravitative forces conflate to pull the ocean's water in the same direction. These tides are known as spring tides Beaver State king tides. The name has nothing to do with the season spring, but instead it is a equivalent word for bound or leap.
An equinoctial spring surge is a give tide that coincides with either the Abut equinox or the September equinox, when the Sun is directly above the Earth's equator. These natural spring tides usually have an even greater tidal range.
Moon phases in your city
Perigean and Apogean Spring Tides
Several times a year, the Full Moon operating theater New Moon happens as the Moon is around its nighest point to Earth, called perigee. This is popularly titled a Supermoon and leads to justified larger variation between high and low tides, known equally perigean resile tides. However, the difference from a normal spring surge is lonesome around 5 cm or 2 inches.
The other happens when the Rumbling or New phase of the moon is around its farthest from Earth, apogee, a.k.a. Micromoon. The apogean spring tides are around 5 cm (2 inches) smaller than regular spring tides.

Neap tide tides at Quarter Moon. (Not to scale.)
©timeanddate.com
Neap tide Tides
The tidal range is smallest around the Quarter Moons /Incomplete Moons because the gravitational storm from the Moon and the Solarise counteract each other at these 2 points of the lunar month. These tides are called neap tides or neaps, from Anglo-Saxon, meaning without the world power. Neaps always occur about 7 days after leap tides.
Oceans and Some Rivers
There is a difference between having noticeable tides and having true tides. For tides to be noticeable, the body of water has to be huge, like an ocean. Even though lawful tides also occur in small water basins, same braggart lakes, the tidal variations here are to a fault small to observation.
For exercise, in the Great Lakes in the US, the largest recurrent event stray is less than 5 cm Beaver State just under 2 inches. Different weather conditions, such as fart and measuring instrument pressure level, creates bigger differences in the water level than tides on these lakes. This is also the suit in the Baltic Sea, the Black Suboceanic, the Caspian Sea, and true the Mediterranean.
Galore rivers copulative to the ocean do take over high and low tides. In some of these tidal rivers, the piddle drains forth almost altogether at low tide, making it possible to walk crosswise the bottom of the river. If a part of a larger river is contrived by the tides, the section studied is known as tidal reach.

Low tide in the river Malta, India.
©iStockphoto.com/zatletic
In few areas, where the tide comes into a narrow bay tree or river, recurrent event bores can form. Created by the next lunar time period, tidal bores are waves which travel against the direction of the water on-line.
Tides in the Soma?
Umpteen populate think that the Moon's gravitation also affects humans, as our bodies are made heavenward of approximately 70% fluid. However, in that location is no scientific evidence supporting this feeling. Compared to the Earth's oceans, the physical body is far too small and contains utmost too midget liquid to experience tides caused by the Moon in whatever meaningful way.
why is there no tides in the mediterranean sea
Source: https://www.timeanddate.com/astronomy/moon/tides.html
Posting Komentar untuk "why is there no tides in the mediterranean sea"